The Secret Social Lives of Giant Poisonous Rats
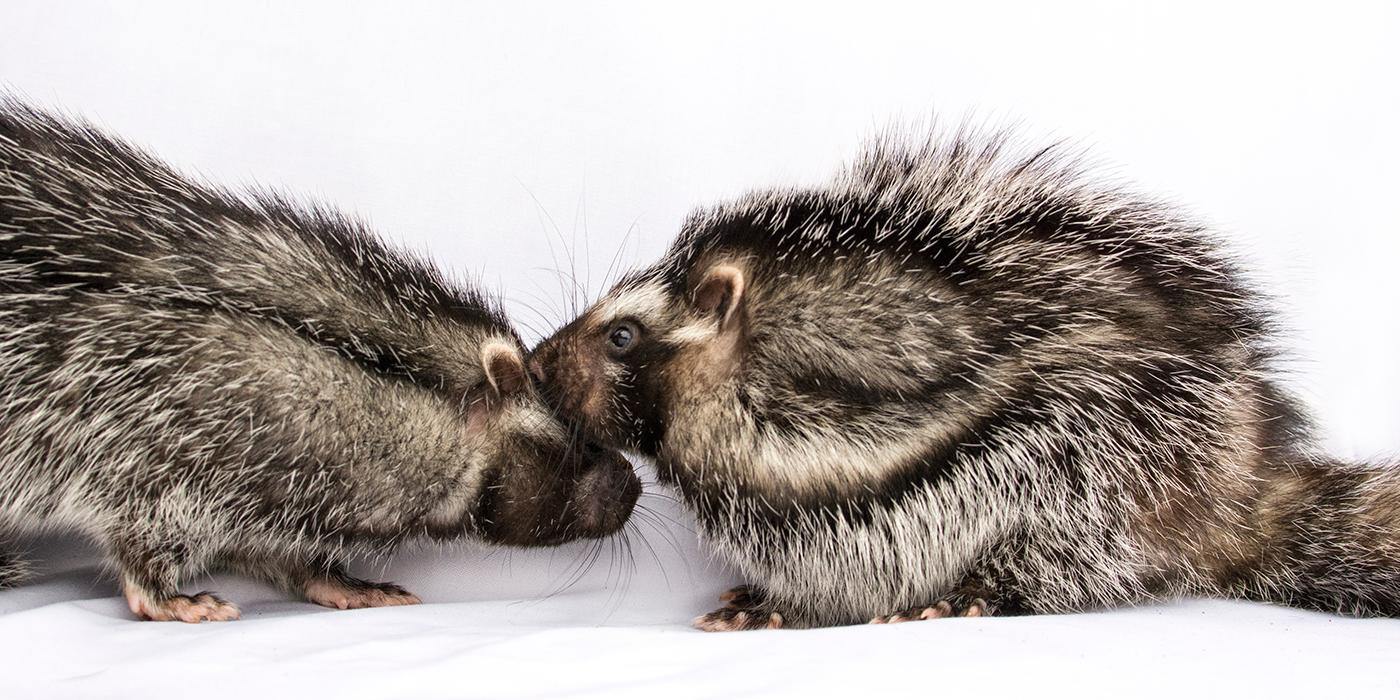

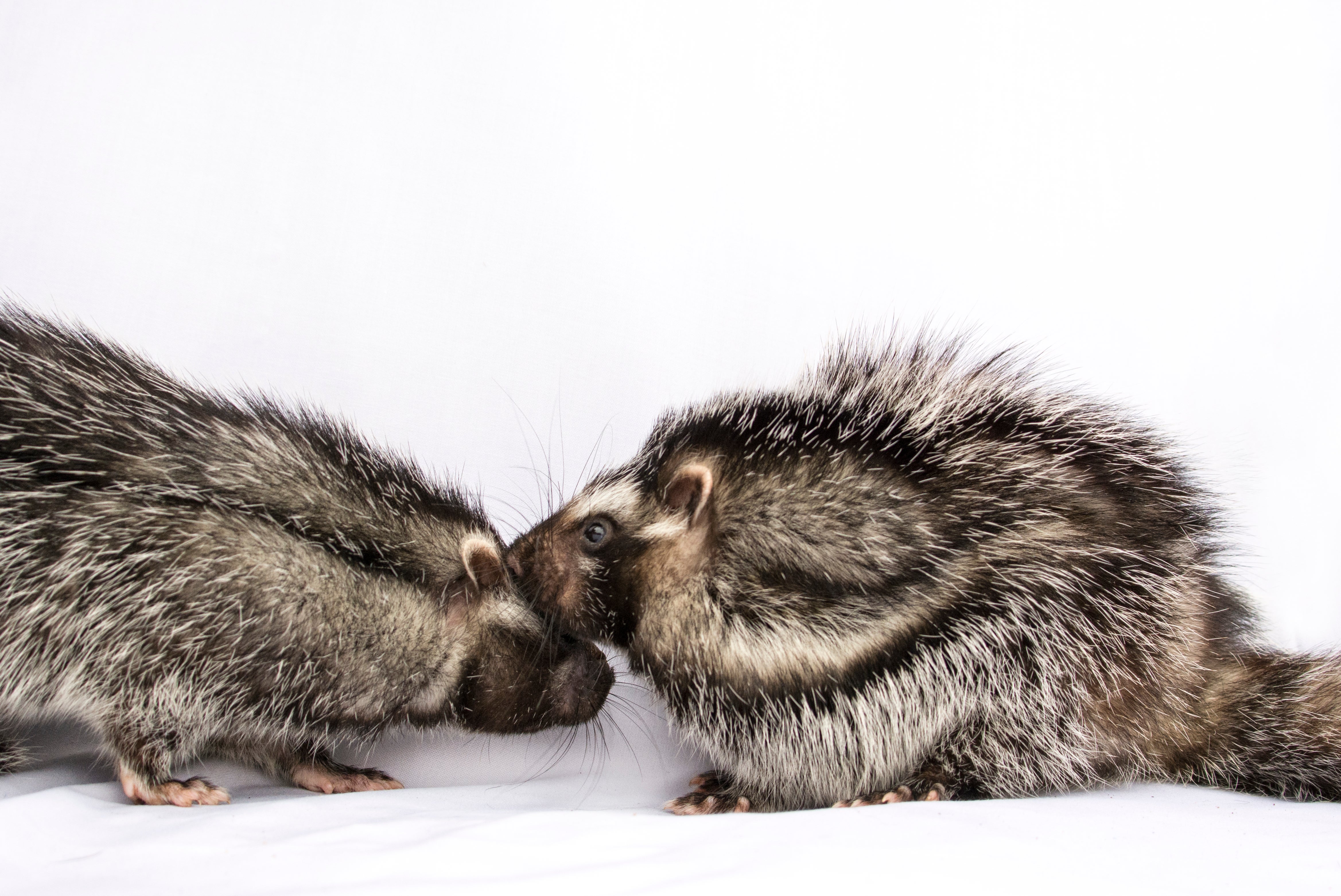
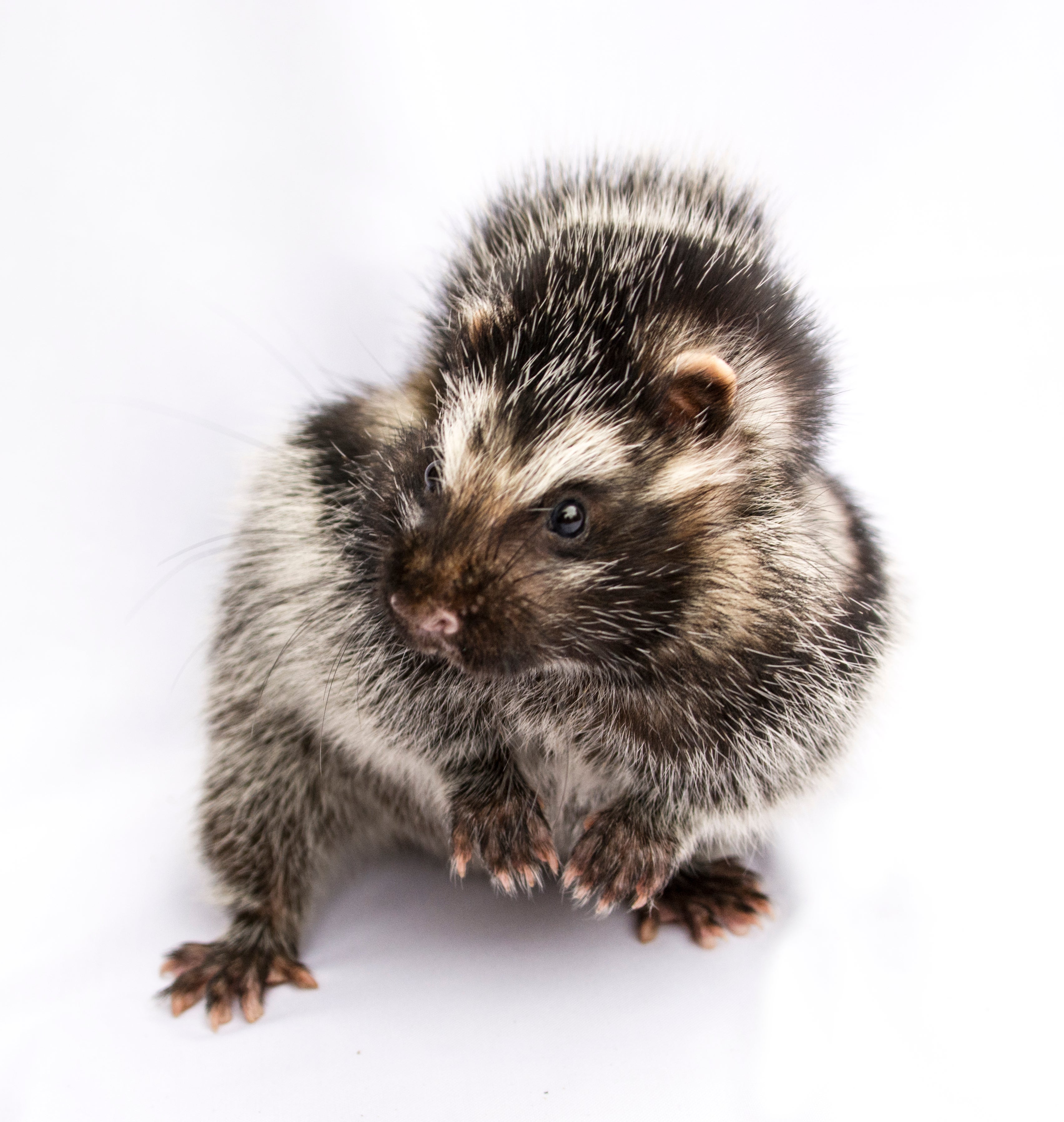
The African crested rat (Lophiomys imhausi) is hardly the continent’s most fearsome-looking creature—the rabbit-sized rodent resembles a gray puffball crossed with a skunk—yet its fur is packed with a poison so lethal it can fell an elephant, and just a few milligrams can kill a human. In a Journal of Mammology paper published yesterday, researchers from the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute, University of Utah and National Museums of Kenya found the African crested rat is the only mammal known to sequester plant toxins for chemical defense, and they uncovered an unexpected social life—the rats appear to be monogamous and may even form small family units with their offspring.
“It’s considered a ‘black box’ of a rodent,” said Sara Weinstein, lead author, Smithsonian-Mpala postdoctoral fellow and postdoctoral researcher at the University of Utah. “We initially wanted to confirm the toxin sequestration behavior was real and along the way discovered something completely unknown about social behavior. Our findings have conservation implications for this mysterious and elusive rat.”
People in East Africa have long suspected the rat to be poisonous. A 2011 paper proposed these large rodents sequester toxins from the poison arrow tree (Acokanthera schimperi). A source of traditional arrow poisons, Acokanthera contains cardenolides, compounds similar to those found in monarch butterflies, cane toads and some heart medications for humans. Cardenolides, particularly the ones in Acokanthera, are highly toxic to most animals.
“The initial 2011 study observed this behavior in only a single individual,” said co-author Denise Dearing from the University of Utah. “A main goal of our study was to determine how common this exceptional behavior was.”
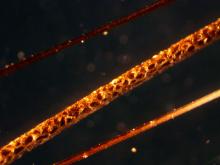
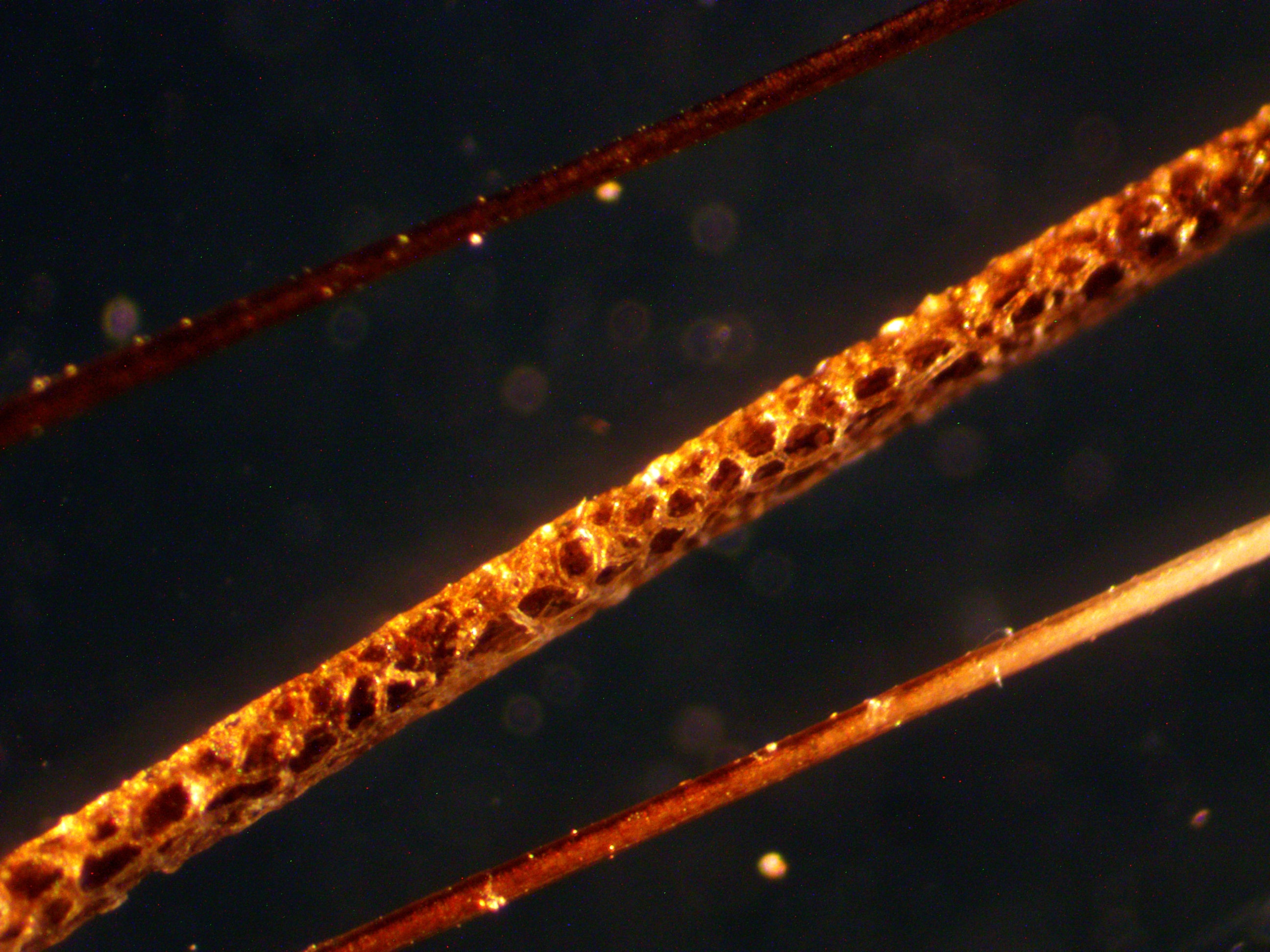
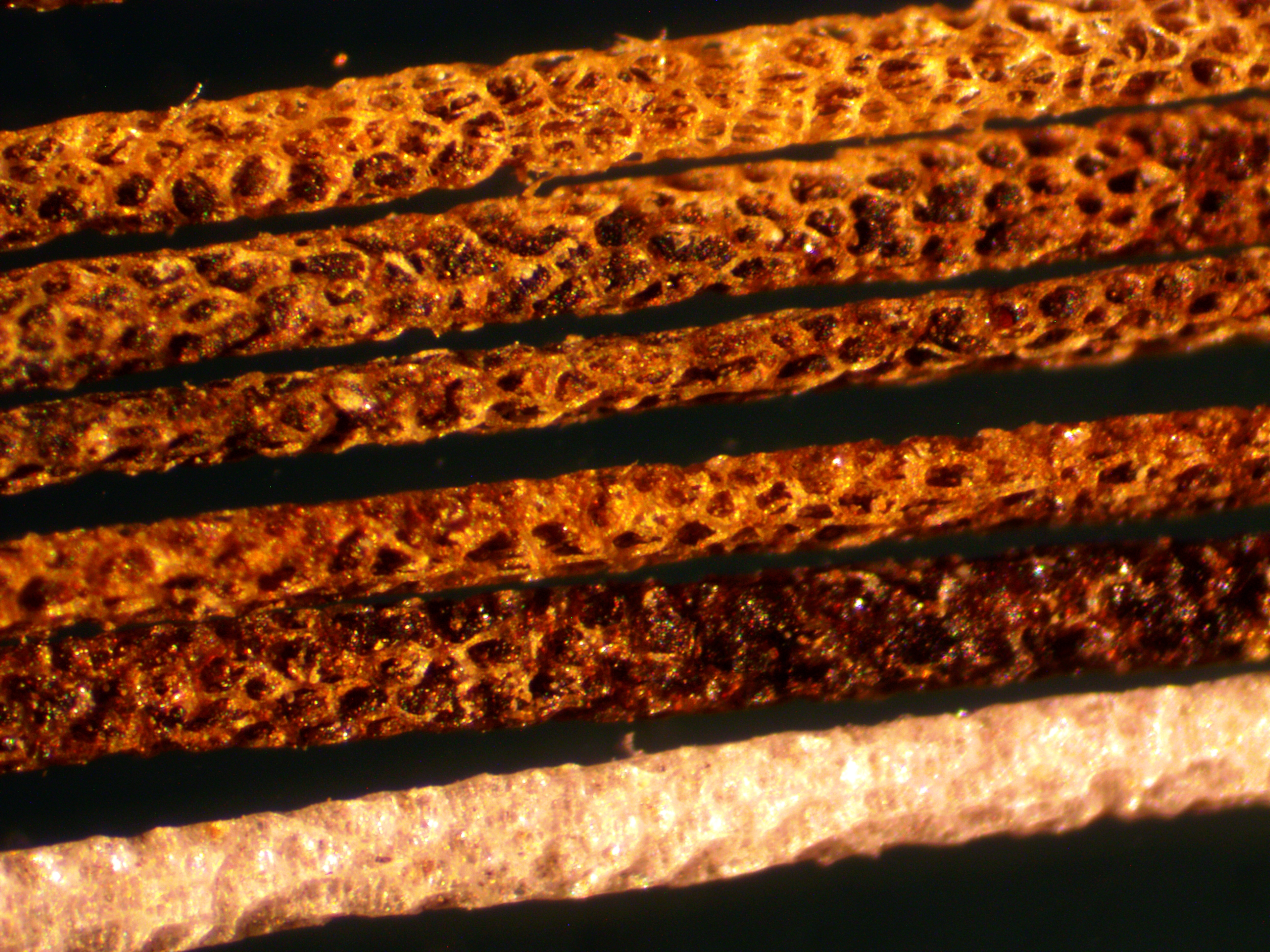
When threatened, the African crested rat lives up to its name and erects a crest of hair on its back to reveal a warning on its flanks—black-and-white stripes running from neck to tail on each side of its body. The 2011 study hypothesized that the rats chew the Acokanthera bark and lick the plant toxins into specialized hairs at the center of these stripes.
In the new study, researchers trapped 25 African crested rats, the largest sample size of the species ever trapped. Using motion-activated cameras, they documented nearly 1,000 hours of rat behavior. For the first time, they recorded multiple rats sequestering Acokanthera toxins and discovered the rats appear to be monogamous and may even form small family units with their offspring.
“Everyone thought it was a solitary animal,” said Bernard Agwanda, curator of mammals at the National Museums of Kenya, co-author of this study and the 2011 paper. “I’ve been researching this rat for more than 10 years, so you would expect there to be fewer surprises. This can carry over into conservation policy.”
A Rich Social Life
As a Smithsonian postdoctoral fellow at the Mpala Research Centre in Kenya, Weinstein first searched for the rats with camera traps, but found that they rarely triggered the cameras. Weinstein was then joined by Katrina Nyawira, the paper’s second author and a graduate student at Oxford Brookes University. Together, they spent months experimenting with live traps to capture the elusive rodents.
“We talked to rangers and ranchers to ask whether they’d seen anything,” said Nyawira. Eventually they figured out that loading the traps with smelly foods like fish, peanut butter and vanilla did the trick. “Out of 30 traps, we finally got two animals. That was a win. This rat is really rare.”
Those two animals changed the course of the study. They first caught an individual female, then caught a male at the same site two days later.
“We put these two rats together in the enclosure and they started purring and grooming each other,” Weinstein said. “Which was a big surprise, since everyone we talked to thought that they were solitary. I realized that we had a chance to study their social interactions.”
Weinstein and Nyawira transformed an abandoned cow shed into a research station, constructing stalls equipped with ladders and nest boxes to simulate their habitat in tree cavities. They placed cameras in strategic spots of each pen and then analyzed nocturnal hours, tracking the total activity, movement and feeding behavior. The aim was to build a baseline of normal behavior before testing whether behavior changed after the rats chewed the toxin cardenolides from the poison arrow tree.
“They’re herbivores, essentially rat-shaped little cows,” Weinstein said. “They spend a lot of time eating, but they walk around, mate, groom, climb up the walls, sleep in the nest box.”
The footage and behavioral observations strongly support a monogamous lifestyle. They share many of the traits common among monogamous animals: large size, a long life span and a slow reproductive rate. In addition, the researchers trapped a few large juveniles in the same location as adult pairs, suggesting that offspring spend an extended period of time with their parents. In the pens, the paired rats spent more than half of their time near each other and frequently followed each other around. The researchers also recorded special squeaks, purrs and other communicative noises making up a wide vocal repertoire. Further behavioral studies and field observation would uncover more insights into their reproductive and family life.
After the researchers established a baseline of behavior, they offered the rats branches from the poison arrow tree. Although the rats did not sequester every time the plant was offered, 10 rats did. They chewed it, mixed it with spit and licked and chewed it into their specialized hairs. Exposure to the Acokanthera toxins did not alter rat behavior and neither did eating milkweed, the same cardenolide-enriched plant used as chemical defense by monarch butterflies. Combined, these observations suggest that crested rats are uniquely resistant to these toxins.
“Most people think that it was a myth because of the potency of the tree,” Nyawira said. “But we caught it on video! It was very crazy.”
The rats were selective about using Acokanthera cardenolides, suggesting that rats may be picky about their toxin source, or that anointed toxins remain potent for a long time, just like traditional arrow poisons from the same source.
African Crested Rat Conservation
The African crested rat is listed as a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, but there is little actual data on the animals. Agwanda has studied African crested rats for more than a decade—and sees indications that they are in trouble.
“We don’t have accurate numbers, but we have inferences,” said Agwanda, who continues to monitor the populations. “There was a time in Nairobi when cars would hit them and there was roadkill everywhere. Now encountering them is difficult. Our trapping rate is low. Their population is declining.”
The research team is planning future studies to better understand the rats’ physiology and behavior. “We are particularly interested in exploring the genetic mechanisms that allow the crested rats and their parasites to withstand the toxic cardenolides” said co-author Jesús Maldonado, research geneticist at the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute and Weinstein’s Smithsonian-Mpala Postdoctoral fellowship co-advisor.
“We are looking at a broad range of questions influenced by habitat change,” Agwanda said. “Humans have cleared forests to make farms and roads. We need to understand how that impacts their survival.” In addition, Agwanda is building an exhibit at the Museums of Kenya to raise awareness about this unique poisonous animal.
About the Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute
The Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute leads the Smithsonian’s global effort to save species, better understand ecosystems and train future generations of conservationists. As Washington, D.C.’s favorite destination for families, the Zoo connects visitors to amazing animals and the people working to save them. In Front Royal, Virginia, across the United States and in more than 30 countries worldwide, Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute scientists and animal care experts tackle some of today’s most complex conservation challenges by applying and sharing what they learn about animal behavior and reproduction, ecology, genetics, migration and conservation sustainability to save wildlife and habitats. Follow the Zoo on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Image Gallery